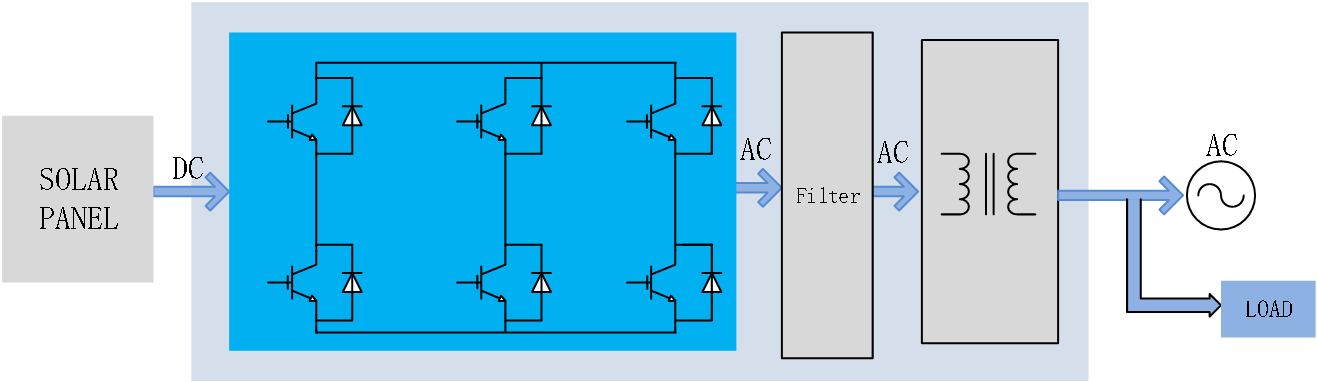
Photovoltaic inverter
Photovoltaic inverters convert power on a single photovoltaic (PV) panel, with a rated power of typically 400W for a single PV panel and up to 1.5KW for multiple PV panels. Photovoltaic inverters are typically based on two-stage power conversion. Firstly, the DC to DC phase or boost circuit converts the variable DC voltage into a fixed DC voltage (usually 40 V-60 V). Meanwhile, maximum power point tracking technology can maximize energy acquisition from photovoltaic panels (usually FSW=100 KHz). Firstly, during the DC to DC conversion phase or boost circuit, the variable DC voltage is converted into a fixed DC voltage (usually 40 V -60 V). Meanwhile, maximum power point tracking technology ensures the extraction of maximum current from the photovoltaic panel. Secondly, during the DC to AC phase, the inverter stage converts the DC power supply into a grid compatible 1 Φ AC power supply. Unlike string inverters, micro inverters can connect one, two, or four photovoltaic panels and perform MPPT tracking on each PV module separately.
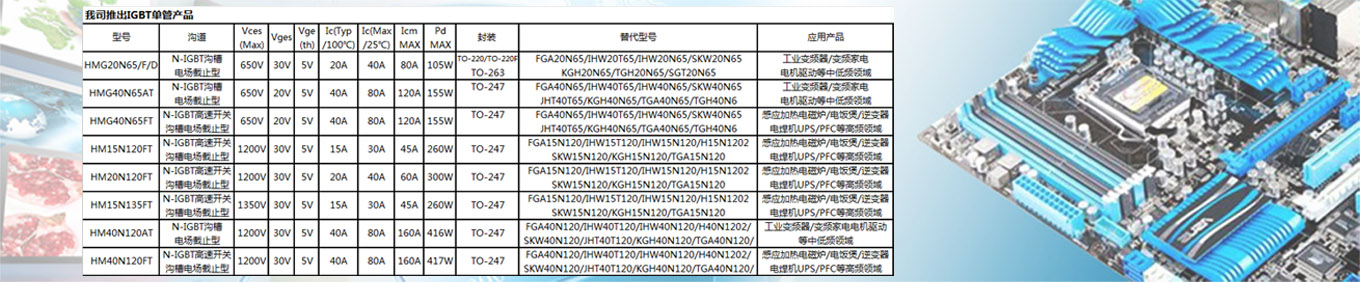
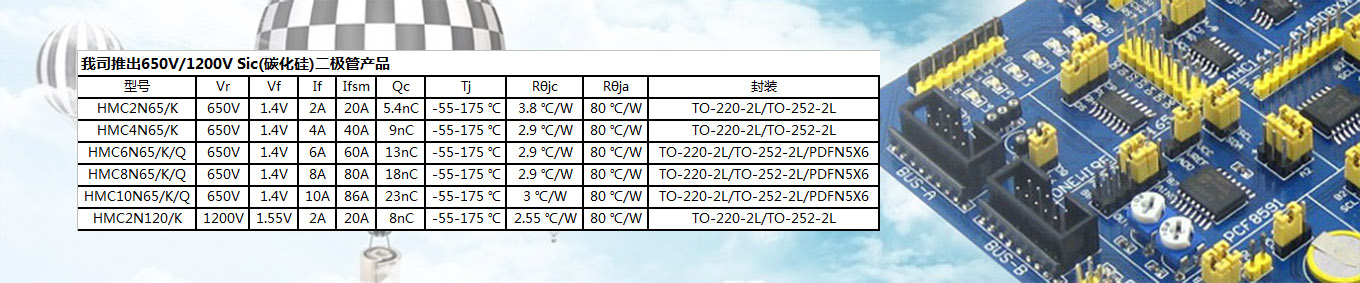
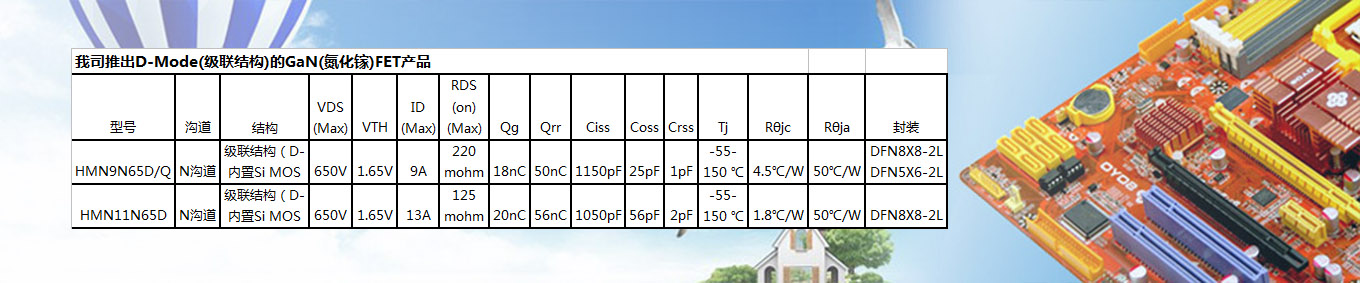
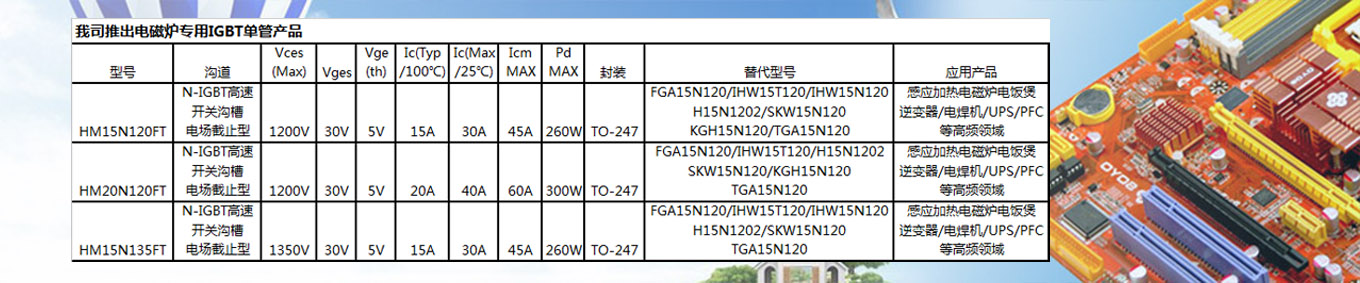
Hongmei utilizes Trench Field Stop IGBT technology and adopts high-density device structure design and advanced ultra-thin chip processing technology to launch a new generation of Trench FS IGBT series products. This series of products significantly reduces device saturation voltage drop and turn off loss by optimizing carrier injection efficiency and carrier distribution, thereby reducing device power consumption and improving system efficiency.